Precautions for foam production enterprises in autumn and winter
The temperature is relatively low in autumn and winter, and the EPS production process is also sensitive to temperature. Recently, many group members have reported that there are problems with many raw materials because they used to be made very light. Now, according to the previous parameter method, the boards are made heavy, cracking, shrinkage, and monetization. And this situation is quite common. So what is the reason for the generally low temperature in winter? Is there really a problem with the raw materials? Or is it due to other reasons? What is the essence behind this?
An important factor that cannot be ignored in autumn and winter - temperature
The board is broken, first we need to check if the bubbles are good? The foam is broken, and the quality of the board is not much better. Generally, when we talk about influencing factors, we tend to focus more on temperature.
The temperature of the foam particles just released from the pre starter is generally 40~50 ℃, and some steam permeates into the foam particles during the pre starter process. The foam particles are relatively wet. After the foam particles leave the pre starter outlet, due to the large temperature difference between the foam particles and the environment, the residual foaming agent and steam inside the foam particles will soon condense into liquid, and the liquid foaming agent will dissolve into the polystyrene foam particles. The internal pressure of the foam particles will soon reduce, and the internal pressure of the foam particles will appear negative pressure (or partial vacuum). At this time, the foam particles appear soft and easily deformed. It is impossible to make EPS foam products at all. It must go through a period of aging.
After maturation, on the one hand, it is dried, and on the other hand, air is infiltrated into the interior of the foam particles to eliminate negative pressure, balance the pressure inside and outside the foam particles, make the foam particles round and elastic, ensure the expansion of the foam particles and the fusion between beads during molding, thereby improving the quality of EPS products.
After understanding the mechanism of pre production and curing, if the insulation effect of the pre production and curing workshop is not good in winter, the temperature is low, the thermal expansion and contraction are easy, and the particle shrinkage is severe, which damages the bubble structure. Therefore, it cannot rebound during curing. If lighter weight boards are made at this time, the boards are prone to shrinkage, cracking, and weight gain. There is an optimal temperature for general curing, with a curing environment temperature of 18-22 ℃. Air infiltrates into the interior of the foam, while the pentane inside the foam does not diffuse outward. When the temperature exceeds 22 ℃, the air infiltration rate increases and accelerates, and at the same time, the speed of pentane diffusion outward also increases; On the contrary, if the temperature is below 20 ℃, the air infiltration rate also decreases significantly, and the maturation time is prolonged. Therefore, the optimal maturation temperature is generally controlled between 20-25 ℃; If the main production is for light board customers, the temperature in the curing workshop can be appropriately increased to around 28 degrees Celsius. (The data is for reference only and subject to actual workshop conditions.)

Everyone knows that in order to make the board light, the foam must be light. In theory, this is possible, but by sorting out the above mechanisms, we can explain why the lighter the foam, the heavier the board?
For example, a lightweight board:
1. One issue: Taking the Fangyuan Guangxing intermittent foaming machine as an example: it was found that it was too heavy. Some workers usually increase the overall pressure to make the foam lighter in order to make the board light enough, which is actually wrong. The higher the pressure, the lighter the task. It depends on the situation. Light boards are usually made in two batches. If one batch is too light, it is easy to cause the bubbles to die during the second batch, making the board heavier. Generally, the cylinder pressure should not exceed 5.5 kilograms, and the intake speed should not be too fast in order to evenly distribute the material.
2. Second round: Pre sent EPS raw materials should generally be placed in a curing chamber with a temperature of no less than 20 ° C and no more than 40 ° C. If the temperature is below 20 ° C, it is easy to not rise up, and if it is above 40 ° C, it is easy to foam and the board will also be heavy when made. Simultaneously, the oxidation time should not be less than 4 hours, followed by secondary foaming. In this way, the weight and quality of the board can be ensured during the board making process. (The data is for reference only, and the actual board production situation shall prevail.)
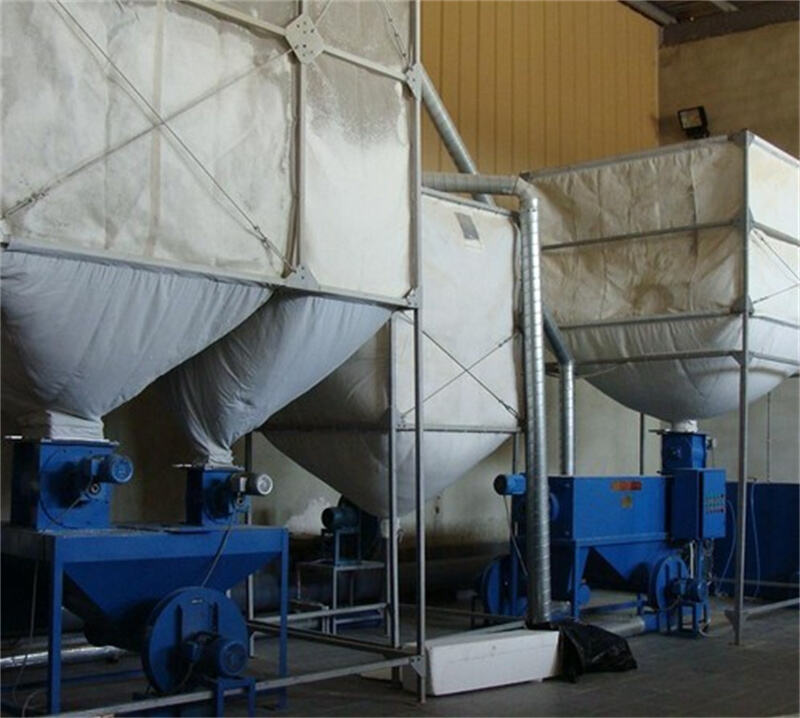

So if the temperature of the curing silo is too low, especially in autumn and winter, when it rains and cools, it may be that the insulation facilities of the foam plant are not well done, and there is air leakage around. The temperature outside the workshop is basically the same as outside, so the foaming agent inside the foam particles is in liquid form and cannot vaporize and expand, resulting in shrinkage of the foam particles and poor hand feel of the finished products. If you want to make light boards, you will actually make them heavier. So in autumn and winter, it is necessary to strengthen the insulation and heating of the silo workshop in order to produce good products.